1 min read
Manhattan Beer and Beverage Distributors Discuss Westfalia’s AS/RS in Modern Material Handling
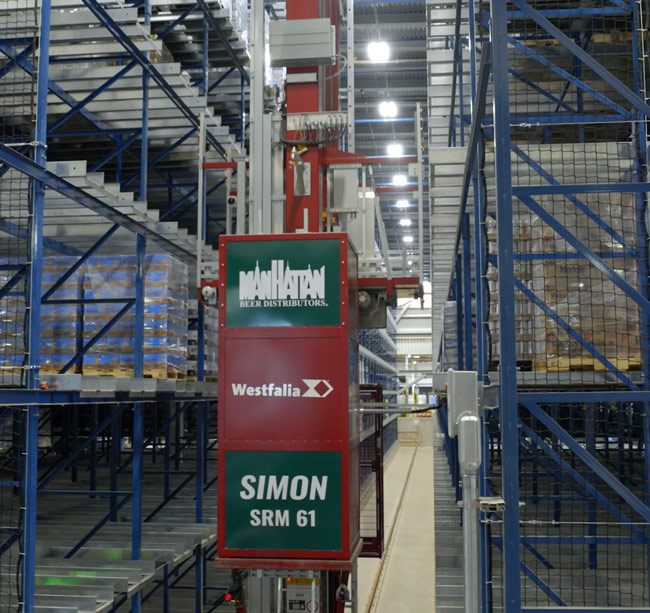
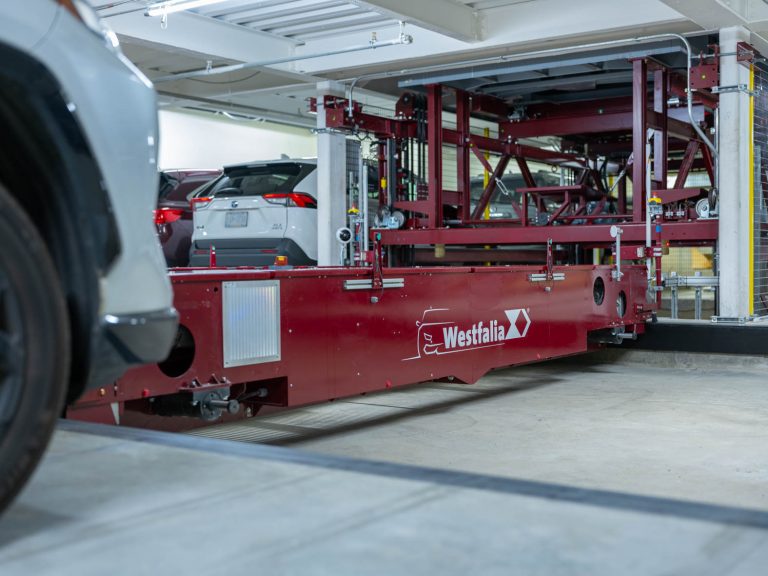
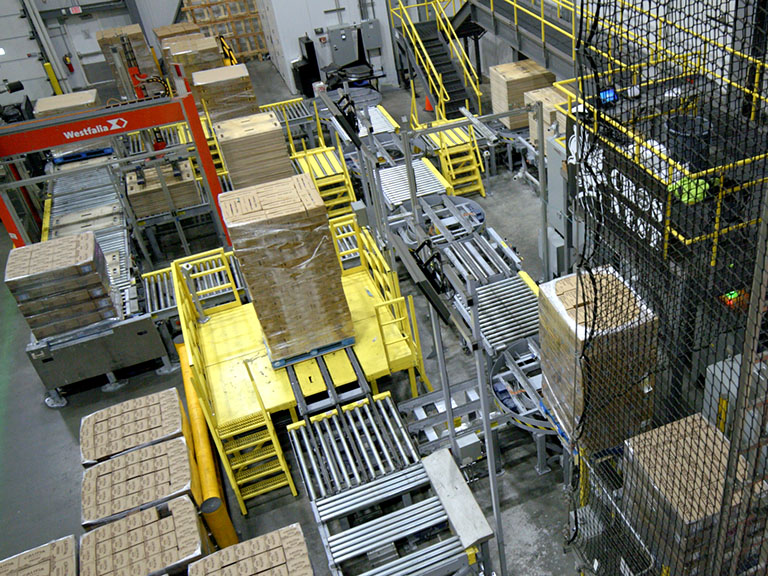
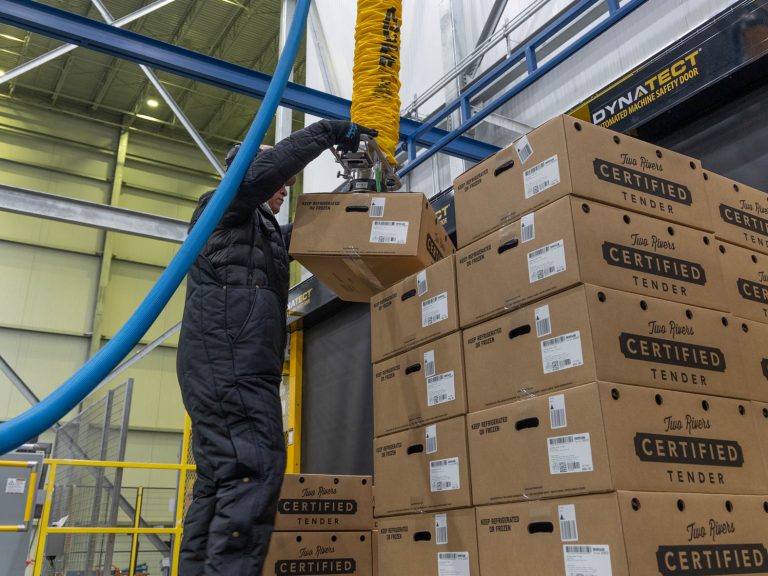
Manhattan Beer & Beverage Distributors has implemented a new pallet AS/RS system that automates and expands their reserve storage capabilities while improving material flow through a major site rebuild. This strategic automation investment boosts network capacity, strengthens regional customer service, and advances their sustainability goals.